Anti-hydrolysis agents are widely used in the polymer industry to improve the stability and durability of polymeric materials in humid environments. Among various polymers, polylactic acid (PLA) and polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) are two promising biodegradable polymers that have attracted considerable attention due to their unique properties and potential applications.

PLA is a thermoplastic aliphatic polyester that can be produced from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane. It is a biodegradable and compostable polymer with excellent mechanical properties and processability, making it an ideal material for a wide range of applications, such as packaging, agriculture, textiles, and medical devices. However, PLA is also susceptible to hydrolysis, which can lead to a decrease in its mechanical properties and biodegradability over time. To address this issue, anti-hydrolysis agents can be added to PLA to improve its stability and durability in humid environments.
PBAT is another biodegradable polyester that is commonly used as a blend component or as a standalone material for various applications, such as packaging, agriculture, and automotive. PBAT is known for its excellent mechanical properties, such as flexibility and toughness, and its ability to biodegrade in different environments. However, PBAT is also susceptible to hydrolysis, which can lead to a decrease in its mechanical properties and biodegradability over time. To overcome this limitation, anti-hydrolysis agents can be added to PBAT to improve its stability and durability in humid environments.
The principle behind the use of anti-hydrolysis agents in PLA and PBAT is to prevent or slow down the hydrolysis reaction by creating a protective layer on the surface of the polymer. Anti-hydrolysis agents typically contain functional groups that can react with water molecules, thereby reducing the availability of water for hydrolysis reactions.
The effect of anti-hydrolysis agents on PLA and PBAT can be evaluated by various methods, such as tensile strength, elongation at break, water absorption, and biodegradability. Studies have shown that the addition of anti-hydrolysis agents can significantly improve the mechanical properties and water resistance of PLA and PBAT, as well as prolong their service life and biodegradability.
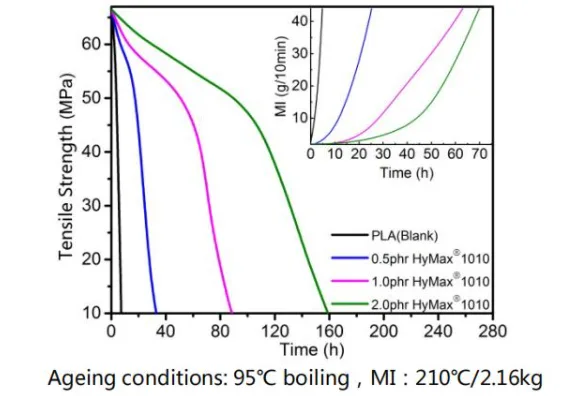
testing result of HyMax anti-hydrolysis agent in PLA
In summary, anti-hydrolysis agents are essential additives for improving the stability and durability of biodegradable polymers such as PLA and PBAT in humid environments. The use of anti-hydrolysis agents can significantly enhance the mechanical properties, water resistance, and biodegradability of these polymers, thus expanding their potential applications and reducing their environmental impact.







