In today’s society, where environmental awareness is on the rise, polylactic acid (PLA) as a renewable and biodegradable alternative has garnered increasing attention. However, despite its many advantages, PLA also faces challenges such as inadequate water resistance and poor thermal stability. To overcome these issues, scientists have developed various types of PLA additives to enhance its performance and expand its applications.
Types of PLA Additives
- Plasticizers: Plasticizers increase the flexibility and elongation of PLA, improving its processing performance and toughness. Common plasticizers include epoxidized soybean oil and epoxidized linseed oil.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidants delay the oxidative degradation of PLA, enhancing its heat resistance and stability, thus prolonging its service life.
- Reinforcements: Reinforcements such as nanoparticles and carbon fibers increase the strength and stiffness of PLA, improving its mechanical properties.
- Fillers: Fillers like cellulose fibers and calcium silicate improve the cost-effectiveness of PLA, reduce its shrinkage, and enhance its surface quality.
- Anti-hydrolysis Agents: Anti-hydrolysis agents are a special type of PLA additive aimed at enhancing its water resistance, delaying its hydrolysis rate, and improving its stability in humid environments. Poly(carbonate di-imine) is a common anti-hydrolysis agent.
Benefits of PLA Additives
- Enhanced Performance: Various types of additives can be tailored to different performance indicators, such as increasing strength, improving heat resistance, and enhancing flexibility, making PLA suitable for a wider range of applications.
- Improved Processing Performance: Additives like plasticizers and fillers improve PLA’s flowability and processability, making it easier to mold and process, thereby reducing production costs.
- Enhanced Environmental Adaptability: Additives such as anti-hydrolysis agents improve PLA’s stability in humid environments, extending its service life and reducing environmental pollution.
Application of Anti-hydrolysis Agents in PLA
Anti-hydrolysis agents are a special type of additive designed to enhance PLA’s performance in high humidity and high temperature environments. In humid environments, PLA is susceptible to hydrolysis, leading to a loss of performance. The introduction of poly(carbonate di-imine) can effectively delay this process and enhance PLA’s stability.
By adding a certain proportion of poly(carbonate di-imine), the water resistance of PLA products can be significantly improved. This widens the range of applications for PLA products, such as in biomedical materials and outdoor packaging in humid environments.
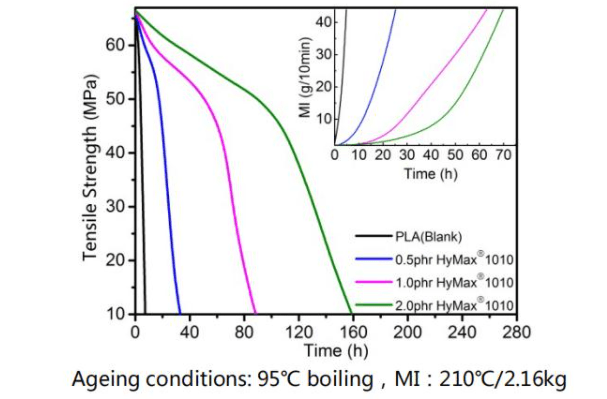
See more about application effect of anti-hydrolysis agent in PLA
In summary, the introduction of PLA additives provides crucial technical support for enhancing PLA’s performance and expanding its applications. In particular, the application of anti-hydrolysis agents and other special additives ensures the stability of PLA in humid environments, driving its widespread use in various fields.







