Introduction
Recently, biodegradable films have garnered considerable interest as an eco-friendly alternative to plastic bags and films. These materials decompose naturally over time to reduce environmental pollution associated with plastic waste disposal. Development has rapidly progressed because of rising environmental concerns and regulatory requirements for them.
Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate
PBAT is an organic synthetic biodegradable polyester known for its excellent flexibility and biodegradability, produced through polymerization of butanediol, adipic acid and terephthalic acid. As its characteristics combine those of both aromatic and aliphatic polyesters, PBAT becomes an appealing choice in many agricultural settings.
Current Applications and Challenges of PBAT Films
- Advantages:
PBAT films degrade naturally in the environment, helping reduce long-term pollution levels and protecting soil health at once.
- Disadvantages of PBAT
Durability Issues: PBAT films often degrade too rapidly and become ineffective in long-term applications.
Hydrolysis Susceptibility: Exposure to moisture accelerates the hydrolytic degradation of PBAT materials, reducing structural integrity and performance significantly.
Hydrolysis Inhibitors
Hydrolysis inhibitors are chemical compounds added to polymers to stop or slow hydrolytic degradation and enhance durability and performance of their materials.
- Chemical Structure
Hydrolysis inhibitors generally consist of functional groups designed to interact with water molecules or intermediate products produced during hydrolysis processes and neutralize or block their pathways of hydrolysis. Hydrolysis inhibitors serve to protect biodegradable polymers like PBAT from moisture degradation, thus prolonging their useful lifespan and upholding mechanical properties.
Utilization of Hydrolysis Inhibitors in PBAT Films
- Increased Durability
Utilizing hydrolysis inhibitors can significantly extend the durability of PBAT films by slowing hydrolysis rate; this allows moisture-resistant films to withstand prolonged moisture exposure without succumbing to structural integrity loss.
- Enhanced Mechanical Properties:
Hydrolysis inhibitors assist PBAT films in maintaining their strength and flexibility for longer, keeping their applications such as agriculture or packaging effective over their lifespan. This guarantees their full effectiveness throughout their intended service lives.
- Add Methods
Hydrolysis inhibitors may be added to PBAT through either powder blending or masterbatch blending methods for consistent protection from hydrolysis. By spreading out their presence evenly within its polymeric matrix, this ensures their presence provides reliable protection.
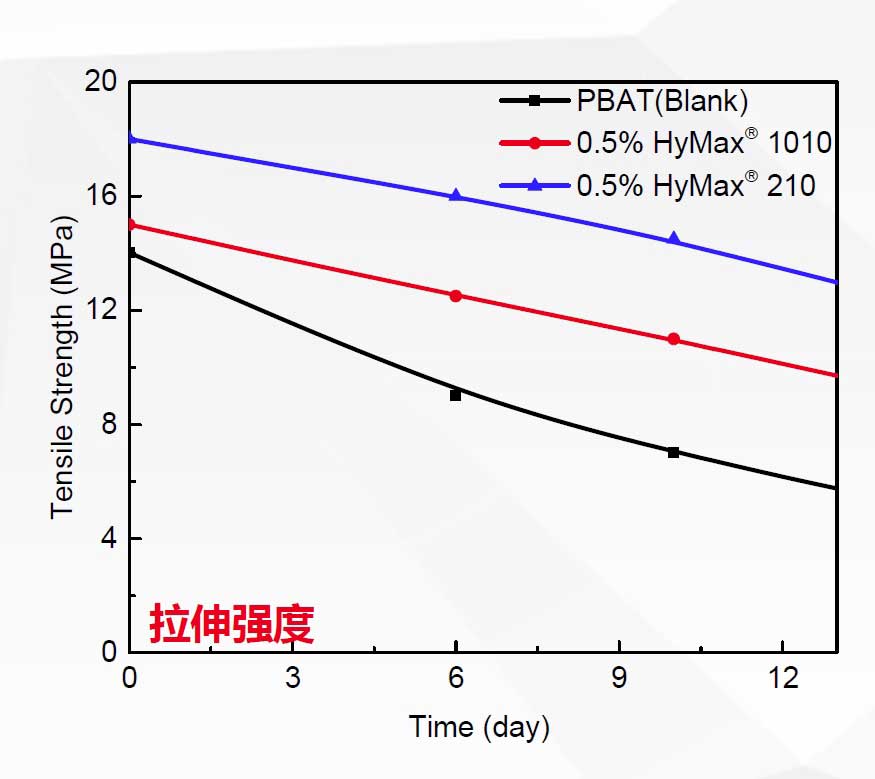
Perfomance of different types of anti-hydrolysis agent in PBAT
Key points of using Hydrolysis Inhibitors—-Even Distribution in PBAT Films
To maximize effectiveness of hydrolysis inhibitors in PBAT film films, they should be distributed uniformly. This ensures all parts receive equal moisture protection thereby improving overall durability. If not mixed uniformly, some areas could remain exposed and lead to weak spots which degrade faster, compromising its overall performance and leading to degradation.
Practical Applications of Hydrolysis Inhibitors in PBAT Films
- Field Mulch Films
In agriculture, polybutadiene terephthalate (PBAT) films have become an indispensable addition to soil covers in modern farms and ranches, helping retain soil moisture, suppressing weeds and maintaining optimal temperature regulation. By including hydrolysis inhibitors into these mulch films as part of the growing season plan they offer long-lasting benefits without degrading prematurely over time.
- Horticultural Covers
PBAT films can also be used in horticulture to protect plants against environmental stresses by covering them and covering with hydrolysis inhibitors that ensure these covers remain effective, providing consistent coverage over the course of their lives.
- Industrial Packaging:
In industrial packaging, PBAT films present an eco-friendly alternative to plastics by increasing durability with hydrolysis inhibitors and providing long-term moisture protection for sensitive products that need long-term storage. They’re particularly ideal for protecting those that must endure fluctuating humidity conditions over an extended period.
- Specialized Applications
hydrolysis-inhibited PBAT films can be tailored specifically for medical packaging where durability and biodegradability are of utmost importance, or used as consumer goods that benefit from increased moisture resistance.
Conclusion
Hydrolysis inhibitors play an integral part in improving and prolonging the performance and lifespan of PBAT films, by protecting against moisture-induced degradation and maintaining their mechanical properties and effectiveness in various applications. Furthermore, hydrolysis inhibitors make these films more viable long-term use while also contributing to environmental sustainability by furthering biodegradable adoption rates. As research and development continue to advance this field, we may expect even more cost-efficient and eco-friendly solutions for biodegradable film applications.







