What is PLA filament material?
PLA filament, also known as polylactic acid filament, is a 3D printing material made from polylactic acid (PLA). The raw material, PLA, is a biodegradable plastic derived from an organic acid called lactic acid, which is usually obtained by fermenting starch from plants. As such, PLA filament is an environmentally friendly and renewable material that is highly sought after by 3D printing enthusiasts.
Why does PLA filament break down?
However, despite its many strengths, such as good printability, low toxicity, and degradability, PLA filament has some weaknesses, one of which is its susceptibility to fracture. The glass transition temperature of PLA materials is low, around 60-65°C. This makes PLA fragile and susceptible to fracture when exposed to high temperatures. In addition, PLA is sensitive to moisture. Excessive humidity can be absorbed by the material and make hydrolysis reaction occur, further affecting the mechanical properties of the material and leading to fracture. (See what is hydrolysis)
How can I make PLA more durable?
First of all, when storing the material, make sure it is kept away from heat and moisture. This can be done by storing it in a moisture-proof box and using a dehumidifier to help absorb moisture from the air.
Second, use modification techniques to enhance the durability of PLA. Adding an anti-hydrolysis agent to polylactic acid (PLA) is an effective way to improve the stability and durability of PLA. This is because PLA is a polymer that is easily hydrolyzed and absorbs water from the surrounding environment, resulting in molecular chain breakage and reduced mechanical properties.
After adding anti-hydrolysis agent, it can play a “barrier” role in the PLA molecular chain, preventing water molecules from attacking the PLA molecular chain and inhibiting its hydrolysis. By forming a stable complex with water molecules, the anti-hydrolysis agent “attracts” the water molecules, making it impossible for them to enter the interior of the PLA molecule for hydrolysis.
In our tests, we found that the addition of anti-hydrolysis agent can significantly improve the hydrothermal stability and durability of PLA, so that the performance of PLA materials in wet environment applications is greatly improved. At the same time, the anti-hydrolyzing agent has little effect on the mechanical and processing properties of PLA, which makes PLA’s ability to be used in biomedical and packaging applications further improved.
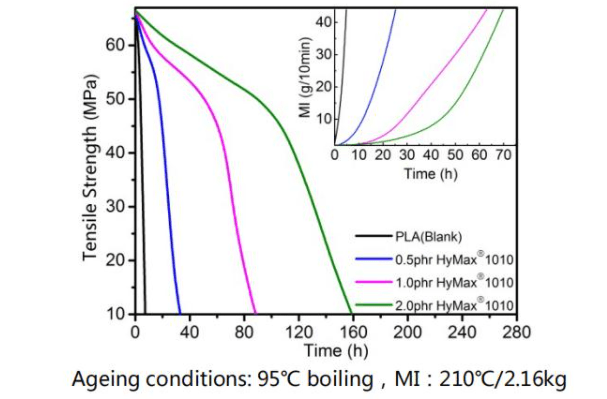
Testing effect of anti-hydrolysi agent in PLA
Overall, the use of anti-hydrolysis agents to optimize the performance of PLA is a very effective strategy, which not only improves the durability and longevity of PLA, but also further expands the application areas of PLA.
Finally, if it is desired to enhance the mechanical strength of PLA filament, a composite approach can be considered. Mixing PLA with other polymers (e.g. ABS, PETG, etc.) or adding some reinforcing materials (e.g. carbon fibers, glass fibers, etc.) can significantly improve its durability and further expand the application areas of PLA filament.
Overall, PLA filament as a “green” 3D printing material, it has a broad application prospect. Through scientific storage and post-processing methods, we can maximize its advantages and flexibly respond to its possible problems, so that the filament can better serve our life and manufacturing.







