Introduction
In the context of growing sustainability and environmental awareness, PLA (Polylactic Acid) as a biodegradable plastic has garnered widespread attention. However, PLA may undergo hydrolytic degradation under specific conditions, affecting its performance and applications. This article delves into the concept of hydrolytic degradation, introduces the basic characteristics and applications of PLA, and discusses how to mitigate PLA’s hydrolytic degradation through the use of anti-hydrolysis agents.

1. What is Hydrolytic Degradation of PLA?
Hydrolytic degradation refers to the breakdown of polymer material chains into smaller molecular units in the presence of water and specific environmental conditions. In the case of PLA, this degradation process involves the cleavage of ester bonds within the polymer’s molecular structure due to the action of water molecules. As a result, the long PLA polymer chains are fragmented into shorter segments, ultimately leading to a reduction in material properties.
2. What is PLA?
PLA is a biodegradable polymer typically derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It is considered an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics. PLA is a thermoplastic material, which means it can be melted and molded when heated, making it suitable for various manufacturing processes.
3. Applications of PLA
Due to its biodegradability, versatility, and ability to be processed into a wide range of forms, PLA finds applications across various fields, including:
- Food Packaging: PLA is used to manufacture biodegradable food containers, utensils, and packaging materials, reducing the environmental impact of single-use plastics.
- Biomedical Devices: PLA is employed in the production of disposable medical devices, including sutures, drug delivery systems, and tissue engineering scaffolds.
- 3D Printing: PLA is a popular choice in 3D printing due to its ease of use, low toxicity, and biodegradability, making it suitable for creating prototypes, artistic projects, and custom-made objects.
4. Mitigating PLA Hydrolytic Degradation
To slow down PLA’s hydrolytic degradation, consider the following strategies:
- Selecting the Appropriate PLA Type: Different PLA formulations exhibit varying levels of susceptibility to hydrolytic degradation. Choosing the right type of PLA for your application can significantly impact its performance and longevity.
- Controlling Environmental Conditions: Hydrolytic degradation occurs more rapidly in high-humidity and high-temperature environments. Thus, it is essential to store and use PLA products in conditions that minimize exposure to moisture and heat.
- Utilizing Anti-Hydrolysis Agents: Anti-hydrolysis additives can be incorporated into PLA formulations to enhance its resistance to hydrolytic degradation. These agents act as protective barriers, slowing down the water-induced degradation process.
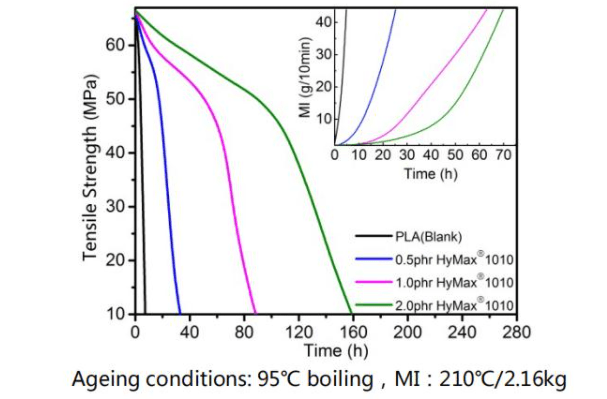
Testing effect of anti-hydrolysis agent HyMax 1010 in PLA
Click to see more about:
Application of anti-hydrolysis agent in PLA/PBAT
Conclusion
PLA, as a biodegradable and versatile material, has gained popularity across various industries. Understanding and managing PLA’s susceptibility to hydrolytic degradation is crucial for maximizing its performance and extending its service life. By carefully selecting PLA types, controlling environmental factors, and incorporating anti-hydrolysis agents, it is possible to mitigate the effects of hydrolytic degradation and harness the full potential of PLA in eco-friendly applications while minimizing its impact on the environment.







