Introduction
Within material science, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) films have emerged as an innovative solution, boasting impressive properties. Their durability and performance characteristics have only increased with anti-hydrolysis agents added as anti-hydrolysis agents further strengthen them extending their use across applications. This article delves deeper into their properties, applications and transformative potential within TPU film applications.
What is Thermoplastic Polyurethane Film (TPU) Film?
TPU film is an extremely durable elastomer material known for its exceptional properties including high abrasion resistance, flexibility and the resistance against oils, grease and solvents.
TPU film can be produced through extrusion, which involves forcing hot TPU resin through a die at high pressure to form a specific thickness film that cools and hardens as soon as it hits room temperature.
TPU film stands out among plastics and rubber in that it combines their best qualities for maximum utility, from elastic properties of rubber to strong durability of plastic – making it suitable for everything from medical devices and athletic apparel to automotive parts and inflatable watercrafts.
TPU film boasts outstanding low-temperature performance and superior mechanical properties; further, its recyclable nature makes it suitable for environmentally conscious applications. Furthermore, this flexible material boasts an array of properties which can be fine-tuned to meet specific product and operational challenges. In all aspects, TPU is an outstanding material choice with many benefits for green applications – especially environmental ones!
Application of thermoplastic polyurethane film
TPU films have found wide application across industries due to their combination of flexibility, toughness, and durability. Here are a few specific examples:
Sporting Goods: TPU film is widely utilized for making air-filled products like soccer balls, water sport equipment, hiking boots and athletic shoes due to its superior wear resistance and flexibility.
Medical Devices: With its biocompatibility, resistance to bacteria growth, and clarity properties, polypropylene makes an ideal material for medical tubing, surgical drapes, wound dressings, and other healthcare products.
Automotive Industry: TPU film can be found used as the material to manufacture car grips, interior trims, protective films for automobile bodies and covers for instrument panels.
Textiles & Fashion: TPU film is used extensively in textile production for weatherproof clothing, accessories and footwear, lamination in fabric structures for added strength as well as laminating fabrics to bolster durability.
Electronics: Due to its resilience and toughness, TPU film is widely utilized for cable jacketing purposes as well as phone cases and other electronic accessories.
Inflatable Structures: TPU film has become an indispensable material used in producing air beds, water/pool toys, inflatable boats/rafts due to its durability and air-holding ability.
TPU film can also be utilized in environmental applications for water and liquid containment, erosion control, transportation of slurries and secondary containment structures.
TPU films’ versatility enables them to provide efficient solutions in numerous applications requiring resistance, flexibility, durability and resistance to oils, chemicals and UV exposure.
What are the disadvantages of TPU?
Although TPU exhibits many impressive properties, like any material it does have some drawbacks:
Hydrolysis and Heat Vulnerabilities of TPU: If TPU is exposed to high temperatures or humidity for extended periods, hydrolytic degradation could take place, distorting its shape while diminishing mechanical attributes like strength or elasticity. Heat can distort TPU’s performance further.
TPU materials tend to have good resistance against certain environmental elements; however, excessive UV radiation exposure may result in color change or reduce overall physical properties of TPU material.
Increased Material Cost: When compared with similar materials, TPU tends to come at a greater expense, potentially altering project budget in high volume applications.
Difficulties in Processing: TPU can be challenging to work with in certain manufacturing, molding or extrusion processes due to its relatively high melting point and higher energy costs during processing.
Color Restriction: TPU materials typically come in clear natural and black colors; to achieve other hues may require ordering large amounts or using additives that alter its properties.
How durable is thermoplastic polyurethane film?
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) films boast an expansive temperature tolerance range, making them suitable for applications across various environments. TPU films typically remain flexible and functional over the entire temperature spectrum – most can maintain their resilience between temperatures as low as -30degC (-22degF) to as high as 80degC (176degF).
TPU characteristics may begin to degrade if exposed to higher temperatures for extended periods, making TPU less suitable for applications exposed to very high heat. Prolonged exposure may cause distortion and reduction of mechanical properties like elasticity and tensile strength of TPU material.
TPU boasts excellent water resistance, performing admirably even under high humidity environments. Unfortunately, overexposure can result in hydrolysis causing irreparable physical properties degradation of this material and eventual degradation.
TPU film can withstand temperatures and humid environments with great resilience; however, depending on its intended use in extreme environments or extreme environments it might require special types of TPU that provide more resilience or other materials that provide alternative solutions such as alternative materials or types of TPU that might provide greater resilience than others.
Antihydrolysis agent in TPU material shows significant anti-hydrolysis protection.
Anti-hydrolysis agents play a vital role in improving the performance of Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) materials. Hydrolysis degradation, caused by exposure to water or high humidity over time, breaks polyurethane bonds which compromise mechanical properties causing reduced performance or failure of parts made of TPU material.
Anti-hydrolysis agents can significantly enhance TPU’s resistance to hydrolysis degradation. Here’s how this affects it:
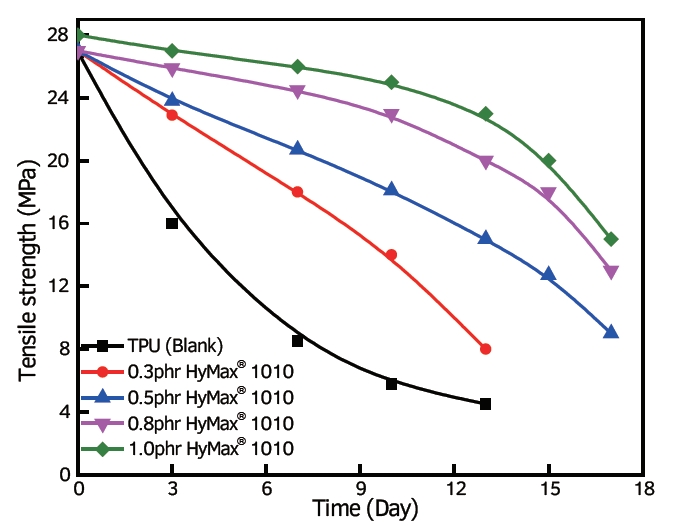
Increased Durability: These agents work to delay or stop polyurethane breakdown and help the TPU maintain its mechanical properties such as strength and elasticity longer.
Extended Lifespan: With anti-hydrolysis agents present, TPU material’s useful lifespan may be extended significantly under damp, hot or humid environments.
Improved Performance: By resisting moisture or water intrusion, TPU parts equipped with these agents maintain efficient functioning over prolonged time periods.
Extended Application Scope: TPUs featuring anti-hydrolysis agents have an expanded application scope thanks to improved hydrolysis resistance, making them suitable for more conditions and environments, further expanding their potential use cases.
See more about application of anti-hydrolysis agent in TPU.
Conclusion
TPU enhanced with anti-hydrolysis agents has revolutionized material performance and durability, surpassing previous expectations in many respects. While certain disadvantages exist, their benefits of increased durability, performance enhancements, extended lifespan and broadened application range make TPU an impressive choice across a variety of applications in industries across the board. The introduction of these revolutionary agents proved transformative making TPU an irreplaceable component.







