High humidity and temperature destroy EVA cables. This threatens performance and safety. How can we protect them?
Anti-hydrolysis agents1 are crucial for EVA cables, especially in humid or high-temperature settings. They prevent material degradation by reacting with water, maintaining cable integrity and extending lifespan. This stops hydrolysis, which can ruin the cable's properties.

We have seen many challenges in material science. One big issue is material degradation. This problem keeps coming up. Now, a solution is available. Let us look at how it works.
What is EVA in cable?
Do high temperatures and humidity affect your cable designs? Have you experienced material failure in challenging environments?
EVA, or Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate, is a popular polymer in cable manufacturing. It has good flexibility, impact resistance, and electrical insulation properties. These make it very useful for many cable applications.
When we started our journey at Langyi, we saw how important material choice is. EVA is an important material in cable insulation and sheathing. It is a copolymer. This means it is made from two different monomers: ethylene and vinyl acetate. The amount of vinyl acetate changes EVA's properties. More vinyl acetate makes it more flexible and adhesive. Less vinyl acetate makes it more like polyethylene.
EVA is used in many industries. You can find it in footwear, solar cell encapsulation, and medical devices. In cables, it is chosen for specific reasons. Its flexibility helps during installation. Its resistance to impact protects the cable from physical damage. It also has good electrical properties. This means it can insulate wires well.
However, choosing EVA is not always simple. Its performance can change depending on the environment. High temperatures and humidity can cause issues. This is something we always consider at Langyi when providing solutions. We help our customers understand these factors.
Here is a simple breakdown of EVA properties based on Vinyl Acetate (VA) content:
| VA Content | Flexibility | Transparency | Adhesion | Hardness | Applications (Cables) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (5-15%) | Moderate | Opaque | Low | High | Wire insulation |
| Medium (15-30%) | High | Translucent | Medium | Moderate | Cable sheathing |
| High (>30%) | Very High | Clear | High | Low | Adhesives, encapsulants |
We, at Langyi, often guide our clients through these choices. Dr. Tang always emphasized understanding the core material deeply. This helps us ensure the cable performs safely and lasts longer.
What are the disadvantages of EVA material?
Do your EVA cables fail prematurely in harsh conditions? Are you struggling with material degradation due to environmental factors?
Despite its benefits, EVA material has limitations. It is prone to hydrolysis, especially in hot and humid environments. This chemical reaction breaks down the polymer chains. It reduces the material's mechanical and electrical properties over time. This can lead to cable failure.
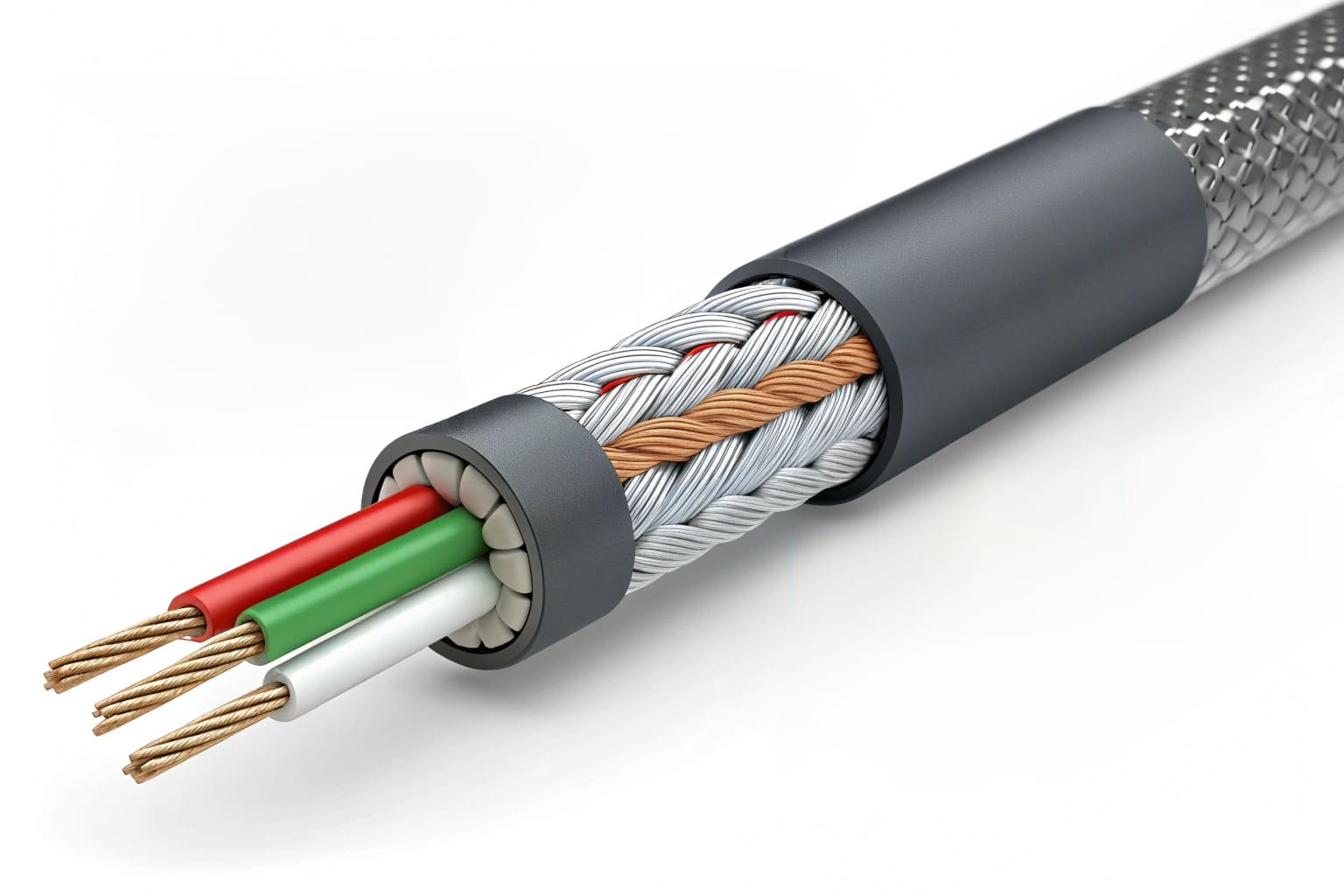
There are many materials in the cable industry. Each has strengths and weaknesses. EVA is no different. One major issue with EVA is its stability in certain conditions. When EVA is exposed to moisture and heat, it can undergo hydrolysis. This is a very common problem in the field.
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction. Water molecules react with the ester links in the vinyl acetate part of EVA. This breaks the polymer chains. When these chains break, the material becomes weaker. It loses its elasticity. Its electrical insulation properties also diminish. Imagine a cable designed to last 20 years failing in 5 because of this. This is a real concern in many applications, like outdoor cables or those used in hot, moist industrial settings.
This degradation is not always visible. It can happen internally. Over time, it can lead to cracking, embrittlement, and eventually, electrical failure. For a company like Langyi, dedicated to providing reliable solutions, addressing this disadvantage is key. We cannot just ignore it.
Here are some direct impacts of EVA hydrolysis on cable properties:
| Property Affected | Before Hydrolysis | After Hydrolysis | Implication for Cable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High | Decreased significantly | Reduced durability |
| Elongation at Break | High | Reduced elasticity | Brittle, cracks |
| Dielectric Strength | Excellent insulator | Decreased | Electrical breakdown risk |
| Volume Resistivity | High | Decreased | Current leakage |
| Water Absorption | Low | Increased | Further degradation |
Understanding these weaknesses helps us find solutions. Our goal is always to improve material performance. This ensures our customers get the best products.
How anti-hydrolysis agent work in EVA cable?
Are you looking for a way to extend the life of your EVA cables in tough conditions? Do you want to protect your investment in cable infrastructure?
At Langyi, our mission is to be a hidden champion. We achieve this by providing expert solutions. When facing EVA hydrolysis, anti-hydrolysis agents are the answer. I remember Dr. Tang explaining the science behind these agents. It is quite ingenious.
These agents are often carbodiimides. They are very reactive. When water tries to attack the EVA polymer, the anti-hydrolysis agent steps in. It reacts with the water molecules first. This prevents the water from breaking down the EVA chains. Think of it as a shield.
Another way they work is by neutralizing the byproducts of hydrolysis. When EVA hydrolyzes, it produces carboxylic acids2. These acids can speed up further degradation. Anti-hydrolysis agents react with these acids. They stop the autocatalytic process. This means they prevent the degradation from getting worse over time.
Adding anti-hydrolysis agents seems complex. But we make it easy for our customers. We offer anti-hydrolysis EVA masterbatches3. This means the agent is already mixed into a polymer carrier. It ensures even dispersion in the final EVA cable compound. This makes the process simple and effective. It guarantees the additive is distributed evenly. This leads to consistent protection across the entire cable.
Here's how anti-hydrolysis agents protect EVA:
| Mechanism | Description | Benefit to EVA Cable |
|---|---|---|
| Water Scavenging | Reacts with water molecules, removing them from the system. | Prevents water from initiating hydrolysis of EVA. |
| Acid Neutralization | Reacts with acidic byproducts (carboxylic acids). | Stops the autocatalytic degradation process of EVA. |
| Polymer Chain Repair (Indirect) | By preventing breakdown, it indirectly maintains chain integrity. | Preserves mechanical and electrical properties over time. |
| Long-term Stability | Provides continuous protection against moisture. | Extends cable lifespan in humid/hot environments. |
Using these agents is not just about extending life. It is about total reliability. It ensures the cable meets its performance specifications for its intended use. This is crucial for safety and operational efficiency. That is why we champion these solutions at Langyi.
Conclusion
Anti-hydrolysis agents are vital for EVA cables. They prevent degradation in humid and hot conditions. This maintains cable performance and extends lifespan significantly.






