What is a papermaking fabric, and what is its function?
A papermaking fabric is a mesh material made of woven polyester monofilament. It is mainly used for filtration and moisture regulation during the papermaking process. In the papermaking process, pulp is pumped into the headbox of the paper machine, where the pressure and spray system evenly distribute the pulp onto the papermaking fabric. Then, through vacuum suction and evaporation of water, the fibers gradually bond together to form paper.
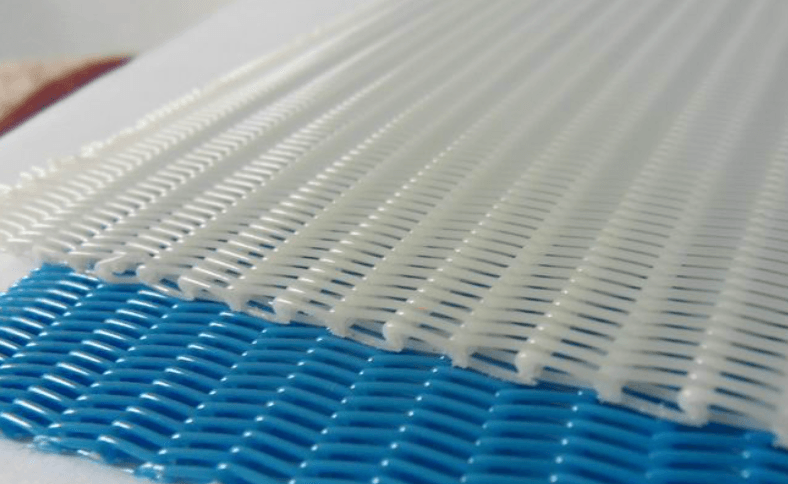
The function of the papermaking fabric is twofold. Firstly, it filters out impurities and solid particles from the pulp, making the paper more uniform in quality and smoother on the surface. Secondly, it regulates moisture by draining excess water through the drainage holes on the fabric, allowing the fibers to bond tightly and enhance the strength and gloss of the paper. Additionally, the mesh size and wire diameter of the papermaking fabric also affect the quality and performance of the paper.
In the process of using papermaking fabric, high-temperature and high-humidity environments can accelerate the hydrolysis reaction of polyester monofilament, resulting in the aging and damage of the fabric, which affects the papermaking quality and production efficiency. Therefore, to extend the service life of the papermaking fabric, it is necessary to add anti-hydrolysis agents to the polyester monofilament.
What is an anti-hydrolysis agent?
An anti-hydrolysis agent is a chemical substance that can effectively suppress the hydrolysis of polyester monofilaments. Its function is to react with hydroxyl compounds in polyester materials, forming compounds that are not easily hydrolyzed by water, thereby preventing material from undergoing hydrolysis reaction.
How to add the anti-hydrolysis agent into polyester monofilament?
The addition of anti-hydrolysis agents is typically accomplished by masterbatch processing, which involves mixing the anti-hydrolysis agent with the polyester monofilament to form an anti-hydrolysis masterbatch, which is then processed into monofilaments and ultimately woven into a papermaking fabric. Since the amount of anti-hydrolysis agent added is relatively small, typically only a small percentage of the weight of the polyester monofilament, it has little impact on the mechanical properties and transparency of the polyester monofilament.
In practical applications, anti-hydrolysis agents have been widely used in the production of various types of papermaking fabrics, such as flat fabrics, mesh fabrics, and extended nip fabrics. These papermaking fabrics are widely used in pulp production, papermaking, printing, and other fields, and can maintain stable filtration efficiency and service life in high-temperature and high-humidity environments.
In conclusion, adding anti-hydrolysis agents is an effective measure to extend the service life of papermaking fabrics. By slowing down the hydrolysis rate of the polyester monofilament, it can reduce maintenance costs and improve papermaking efficiency and quality.